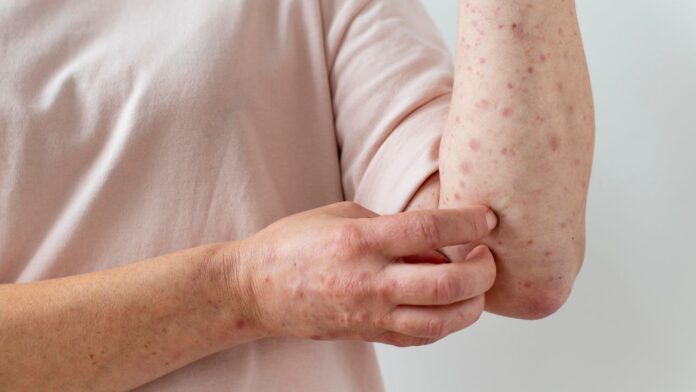
Monsoon season can be particularly challenging for those prone to infections and allergies. During this time of year, people often fall ill due to rapidly changing weather conditions. The increased dampness and humidity in the air create an ideal environment for bacteria and fungi, leading to various infections. Eye infections, such as conjunctivitis, styes, and fungal infections, are especially common during the monsoon. Additionally, skin allergies, including dermatitis, ringworm, dry skin, and scabies, see a significant rise.
Scabies is a type of skin allergy characterized by intense itching and rash. It is a parasitic infestation caused by mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs. If left untreated, scabies can lead to serious health complications such as septicemia, heart disease, and kidney problems.
Here are some prevention measures to manage scabies:
- Maintain personal hygiene: Take regular baths with warm water and mild soap. Clean and dry yourself immediately after getting wet in the rain. Avoid sharing personal items like towels, clothing, and bedding with others.
- Clothing and bedding care: Wash clothes, bed linens, and towels in hot water and dry them in a hot dryer after use. Frequently change bed linens and clothes.
- Environmental cleaning: Regularly vacuum living areas, especially carpets, upholstery, and mattresses. Clean and disinfect commonly touched surfaces to reduce the risk of mite spread.
- Avoid close contact: Limit physical contact with infected individuals until they have completed treatment.
- Use anti-scabies medication: Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate scabies treatment, typically involving topical creams or oral medication. Follow the prescribed treatment regimen strictly to ensure complete eradication of mites.
- Treat all household members: Even if only one person shows symptoms, it’s advisable to treat all household members to prevent the spread of scabies. Ensure pets are also checked and treated, as they can sometimes harbor mites.
- Manage symptoms: Use soothing lotions like calamine or antihistamines to alleviate itching as recommended by a healthcare provider. Avoid scratching, as it can lead to secondary infections.
- Seek medical advice: If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a dermatologist for specialized care.

 हिंदी
हिंदी