Heart attacks, strokes, and coronary artery disease are just a few of the disorders that affect the heart and blood arteries, and cardiovascular disease is the largest cause of mortality in the world, taking millions of lives every year. In order to stop the emergence of cardiovascular disease and manage its effects on our health, it is essential to understand the risk factors connected with it.
The dangers of cardiovascular disease include:
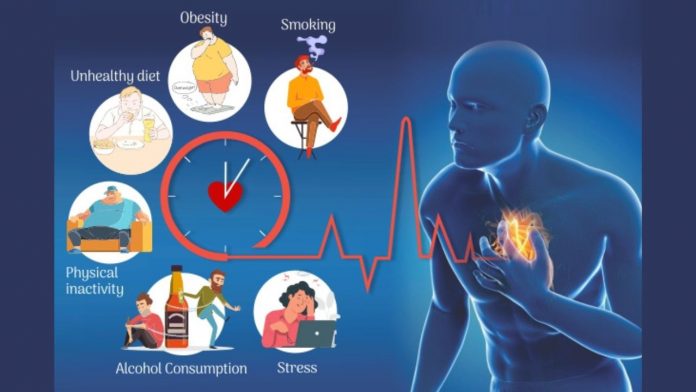
Smoking is a significant cardiovascular disease risk factor. Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that can harm blood vessels and lessen the quantity of oxygen that the heart muscles receive, raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Hypertension, often known as high blood pressure, is another important risk factor. Uncontrolled high blood pressure strains the arteries over time, weakening them, and increases the risk of blockages in critical organs like the heart or brain. A heart attack may result from stress on the heart.
Additionally significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease include obesity and inactivity. While carrying extra weight strains the heart and raises cholesterol levels, a sedentary lifestyle over time weakens the cardiac muscles. Furthermore, a diet heavy in sodium, cholesterol, and saturated fats might hasten the development of arterial plaque and raise the risk of cardiovascular issues later in life.
To obtain energy, the human body needs glucose or sugar. The pancreas-produced hormone insulin facilitates the movement of glucose from the food we eat to the body’s cells where it is used as fuel. In those with diabetes, the body is either unable to use its own insulin effectively or does not create enough of it. Diabetes consequently causes a buildup of sugar in the blood. Compared to adults without diabetes, persons with diabetes have a higher risk of dying from heart disease. Early identification of these risk factors enables people to take proactive measures to adopt healthier lifestyle choices that support optimum cardiovascular health.
Prevention advice for cardiovascular disease:
The most important thing to do is start eating a balanced diet. The risk of heart disease is decreased by including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats in your meals in addition to supplying necessary nutrients. Another important element in preventing cardiovascular problems is regular exercise. Exercises that enhance circulation and strengthen the cardiac muscles include walking, running, swimming, or cycling for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
Additionally, keeping a healthy weight is good for the heart. Being overweight strains the heart and raises the risk of diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure, which can advance heart disease. The prevention of heart disease often involves stress management.

 हिंदी
हिंदी