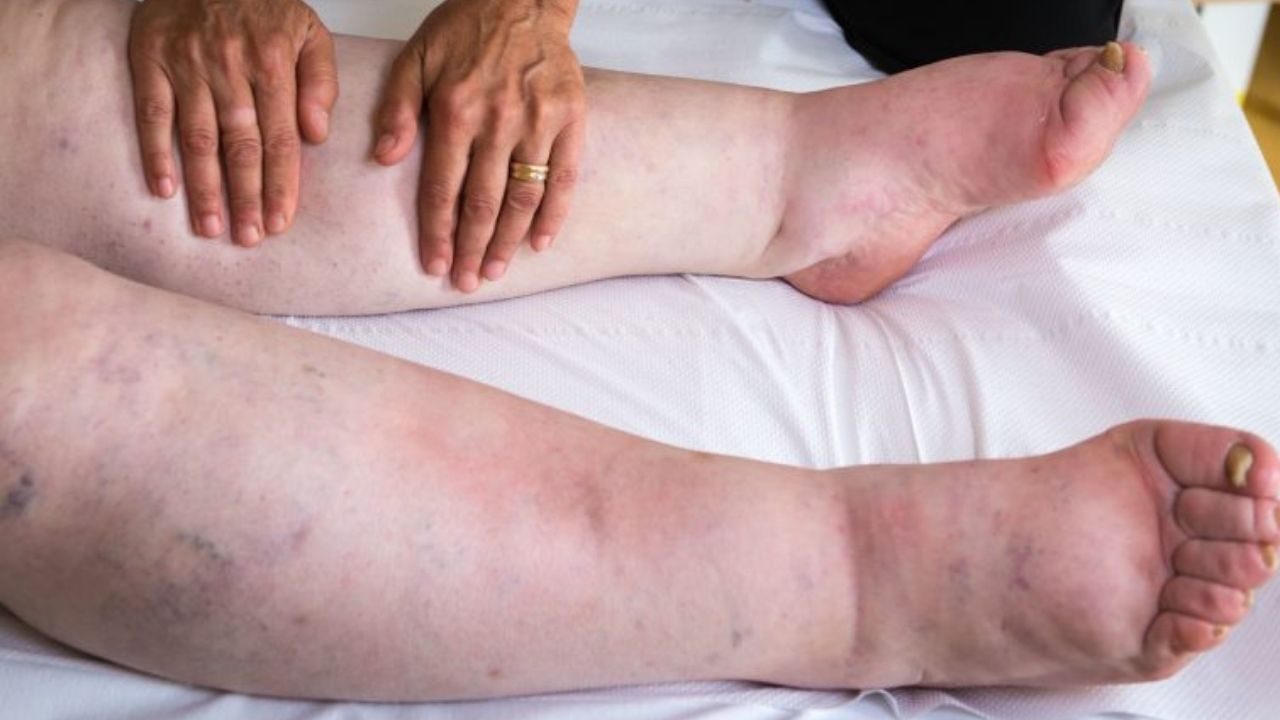
Treatment for breast cancer comes with its own set of side effects, which include nausea, exhaustion, discomfort, and numbness, among other things. While some of them are simple to control, others, such as lymphedema, are more difficult. Lymphedema is a typical side effect of breast cancer therapy, and it can develop days, months, or even years after the procedure. Swelling in your arm, leg, or any other body area that is persistent and extreme should not be disregarded. Lymphoma symptoms can range from minor to severe, and it can make it difficult to carry out everyday tasks owing to difficulties moving and agonizing discomfort.
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system, which transports extra fluids around the body, malfunctions. As a result, the fluid tends to accumulate, resulting in soft tissue swelling or lymphedema. Primary lymphedema is caused by hereditary or genetic causes, whereas secondary lymphedema is caused by an injury or blockage. Furthermore, the majority of secondary lymphedema instances result from cancer or breast cancer therapy, according to a Breast Cancer Surgeon.
Lymphedema symptoms
The following are lymphedema symptoms that might occur after breast cancer treatment:
Breast cancer-related lymphedema affects mostly the arm, beginning at the back of the palm and advancing upwards. It might happen days or years after you start taking the medication.
Breast cancer-related lymphedema causes
The removal of axillary (armpit) lymph nodes, radiation therapy to underarm lymph nodes leading to scarring and blockage of the lymphatic system, cancer involving a large number of lymph nodes, mastectomy, and scar tissue near lymph nodes that interferes with the lymphatic system are all treatment-related risk factors for this condition.
After being diagnosed with breast cancer and receiving treatment for it, diabetes, obesity, and smoking might exacerbate this disease.

 हिंदी
हिंदी