The upcoming commencement of the holy month of Ramadan, just a few days away, marks a period of spiritual contemplation, self-control, fasting, and devotion for Muslims worldwide. Engaging in fasting during Ramadan offers various advantages, such as providing the digestive system with essential rest, preventing metabolic disorders, and detoxifying the body. These practices contribute to the reduction of blood pressure and cholesterol levels. However, individuals with diabetes undertaking Ramadan fasting must exercise caution by implementing necessary dietary and lifestyle adjustments to avert blood sugar spikes and potential complications. One health risk for those with diabetes during fasting is the occurrence of hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels due to the absence of food and water.
Guidelines for effectively managing diabetes during Ramadan fasting include:
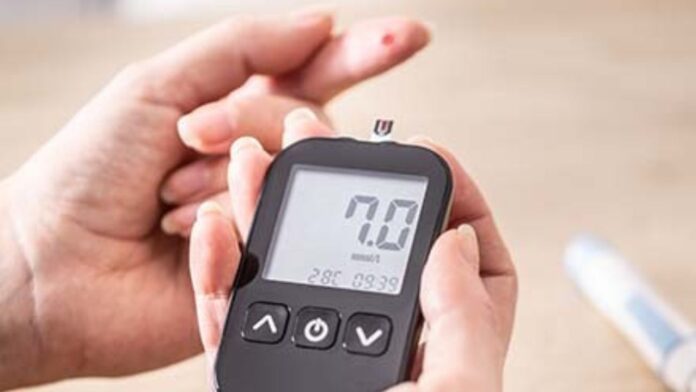
- Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to prevent complications.
- Be vigilant for signs such as dizziness, blurry vision, or irregular heartbeat; cease fasting immediately if symptoms arise.
- Ensure hydration by consuming water during Suhoor and Iftaar, aiming for 8-10 glasses in total.
- Limit exposure to outdoor conditions, particularly in hot environments; prioritize staying indoors whenever possible.
- Avoid overeating during Iftaar to prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Incorporate moderate exercise into your routine, selecting activities suitable for your fitness level while avoiding strenuous workouts.
- Consult with your dietitian or doctor about your fasting plans, informing them of your intentions, as adjustments to medication or treatment may be necessary during Ramadan.

 हिंदी
हिंदी